Python3.14 Highlights 🙌
目录:
之前在欧特克帮忙面试印度同胞时,为了暖场,我有时会询问面试者他们最喜欢的 Python3 新特性是什么。有趣的是一半以上的人会一时语塞,瞬间反作用冷场到零度了。
而我认识的优秀程序员往往有一种“怪癖”,新版本发布后,会兴奋的迫不及待阅读 release note,并第一时间选择更新。
让我们跟着 Anthony 快速了解一下 Python3.14 版本的主要更新与改进:
列表:
1)命令行 REPL 支持语法高亮
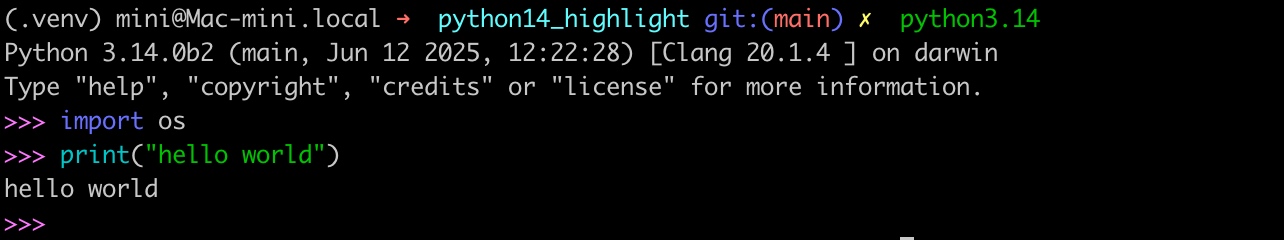
以及 json & calendar 等模块对应的改进:
# json
python3.14 -m json demo.json
# calendar
python3.14 -m calendar
# argparse
> parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(color=True)
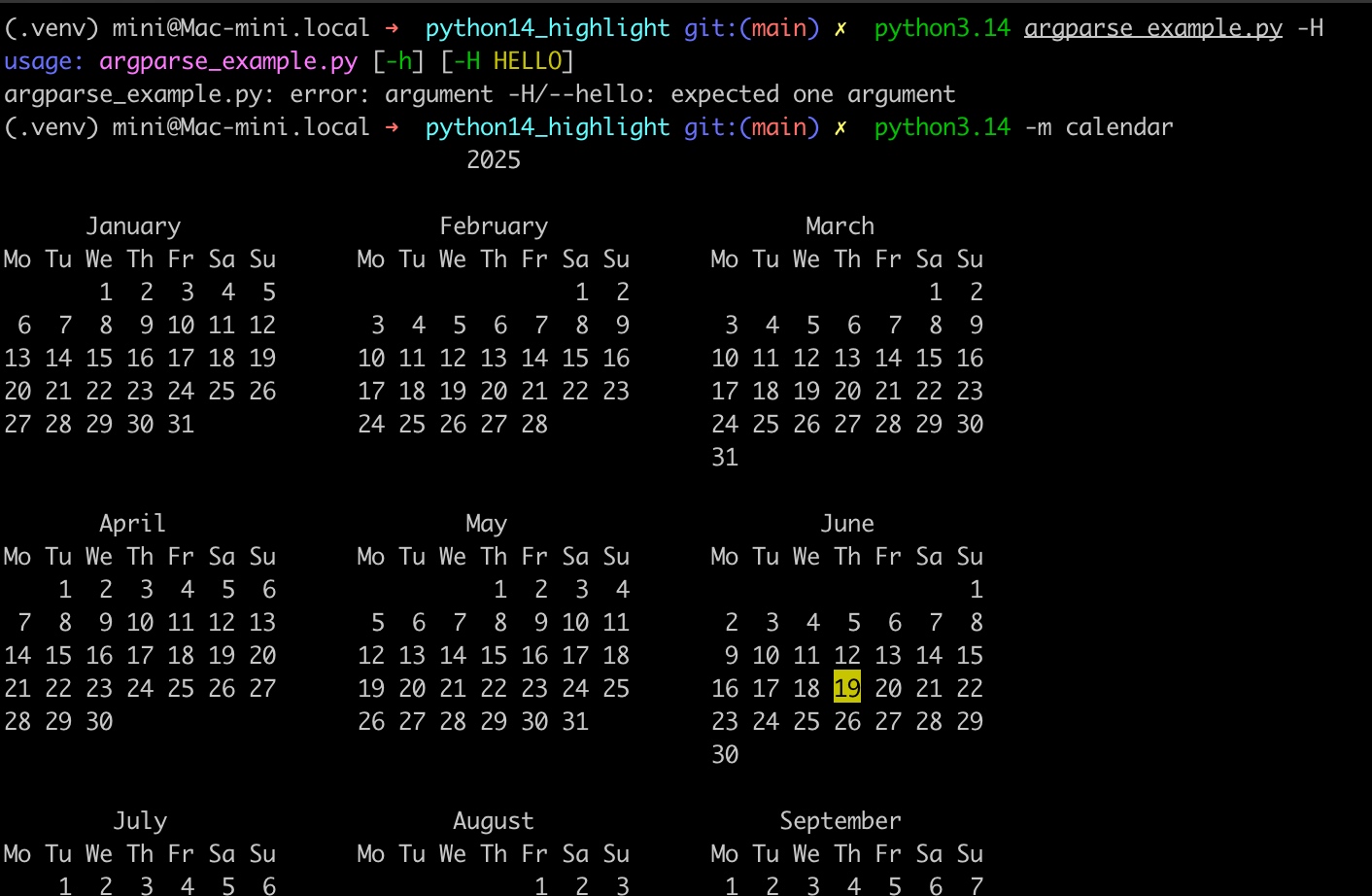
p.s. 不太懂程序员的审美,五颜六色花里胡哨的。
2)PEP 765: 新的 finally 代码块警告
避免在 finally 中使用 return、break 和 continue
example.py:14: SyntaxWarning: 'return' in a 'finally' block
return 1
3)PEP 758:新的异常处理语法
允许不带括号的 except 和 except* 表达式:
# before
try:
raise AssertionError("hi")
except (AssertionError, ValueError):
pass
# after
try:
raise AssertionError("hi")
except AssertionError, ValueError:
pass
有趣的是作者联想到在 python2 中存在类似的语法 except AssertionError, e: XD
4)PEP 750:模板字符串(t-strings)
与 f-string 类似,但返回 Template 而不是 str:
from string.templatelib import Template
name = "World"
template: Template = t"Hello {name}"
进而方便通过编写自定义的模版处理程序,避免 html/sql 注入等问题:
from string.templatelib import Template, Interpolation
def lower_upper(template: Template) -> str:
"""Render static parts lowercased and interpolations uppercased."""
parts: list[str] = []
for item in template:
if isinstance(item, Interpolation):
parts.append(str(item.value).upper())
else:
parts.append(item.lower())
return "".join(parts)
name = "world"
assert lower_upper(t"HELLO {name}") == "hello WORLD"
5)PEP 649:类型注解延迟评估(lazily evaluated)
注意下面代码中 make 方法返回的 C,无需再使用引号来避免 NameError:
class C:
@classmethod
def make(cls) -> C:
return cls()
从反编译的字节码中可以看到区别(看的懂的朋友可以分析一下这段代码的含义):
python3.14 -m dis t.py
...
> Disassembly of <code object __annotate__ at 0x102437780, file "t.py", line 3>:
> -- COPY_FREE_VARS 1
>
> 3 RESUME 0
> LOAD_FAST_BORROW 0 (format)
> LOAD_SMALL_INT 2
> COMPARE_OP 132 (>)
> POP_JUMP_IF_FALSE 3 (to L1)
> NOT_TAKEN
> LOAD_COMMON_CONSTANT 1 (NotImplementedError)
> RAISE_VARARGS 1
> L1: LOAD_CONST 1 ('return')
> LOAD_DEREF 1 (__classdict__)
> LOAD_FROM_DICT_OR_GLOBALS 0 (C)
> BUILD_MAP 1
> RETURN_VALUE
并且新引入 annotationlib 在 runtime 对 annotation 进行交互:
import annotationlib
class C:
@classmethod
def make(cls) -> C:
return cls()
print(annotationlib.get_annotations(C.make)) # output: {'return': <class '__main__.C'>}
6)PEP 784:将 Zstandard 加入标准库
Zstandard(简称:zstd)是由 Facebook 开发的一种无损数据压缩算法,下面是它的用法:
>>> import compression.zlib
>>> text = b"banana apple banana apple banana"
>>> print(f"original size: {len(text)}")
original size: 32
>>> print(f"compressed size: {len(compression.zlib.compress(text))}")
compressed size: 22
>>>
详情请参考:https://peps.python.org/pep-0784/
7)PEP 768:全新的无侵入式远程调试
无需设置断点,例如 break(),直接 attach 至正在运行的进程进行 debug
看起来有点吓人,通过 pid 与 script 参数就可以控制正在运行的 python 进程。
>>> import sys
>>> help(sys.remote_exec)
Help on built-in function remote_exec in module sys:
remote_exec(pid, script)
Executes a file containing Python code in a given remote Python process.
但真正尝试后,与 gdb 类似是相对安全的,需要特定的权限:
python3.14 -m pdb -p 94414
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<frozen runpy>", line 198, in _run_module_as_main
File "<frozen runpy>", line 88, in _run_code
File "/Users/mini/.local/share/uv/python/cpython-3.14.0b2-macos-aarch64-none/lib/python3.14/pdb.py", line 3610, in <module>
pdb.main()
~~~~~~~~^^
File "/Users/mini/.local/share/uv/python/cpython-3.14.0b2-macos-aarch64-none/lib/python3.14/pdb.py", line 3541, in main
attach(opts.pid, opts.commands)
~~~~~~^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "/Users/mini/.local/share/uv/python/cpython-3.14.0b2-macos-aarch64-none/lib/python3.14/pdb.py", line 3425, in attach
sys.remote_exec(pid, connect_script.name)
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
PermissionError: Cannot get task for PID 94414
强行使用 root 执行
sudo python3.14 -m pdb -p 11996
> /Users/mini/.local/share/uv/python/cpython-3.14.0b2-macos-aarch64-none/lib/python3.14/selectors.py(398)select()
-> fd_event_list = self._selector.poll(timeout)
(Pdb) p timeout
500
(Pdb)
当然如果还还是存在顾虑,可以通过环境变量将这个功能关闭。
aysncio 调试
参考官方 demo 的例子:https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3.14/whatsnew/3.14.html#asyncio-introspection-capabilities
看上去挺酷,不知是否实用:
python -m asyncio pstree 12345
└── (T) Task-1
└── main example.py:13
└── TaskGroup.__aexit__ Lib/asyncio/taskgroups.py:72
└── TaskGroup._aexit Lib/asyncio/taskgroups.py:121
├── (T) Sundowning
│ └── album example.py:8
│ └── TaskGroup.__aexit__ Lib/asyncio/taskgroups.py:72
│ └── TaskGroup._aexit Lib/asyncio/taskgroups.py:121
│ ├── (T) TNDNBTG
│ │ └── play example.py:4
│ │ └── sleep Lib/asyncio/tasks.py:702
│ └── (T) Levitate
│ └── play example.py:4
│ └── sleep Lib/asyncio/tasks.py:702
└── (T) TMBTE
└── album example.py:8
└── TaskGroup.__aexit__ Lib/asyncio/taskgroups.py:72
└── TaskGroup._aexit Lib/asyncio/taskgroups.py:121
├── (T) DYWTYLM
│ └── play example.py:4
│ └── sleep Lib/asyncio/tasks.py:702
└── (T) Aqua Regia
└── play example.py:4
└── sleep Lib/asyncio/tasks.py:702
8)Misc
视频中提到的其他微小更新:
# 新的 operator 方法 is_none/is_not_none
>>> import operator
>>> operator.is_none(1)
False
>>> operator.is_none(None)
True
>>>
# 新的 ast 方法 compare
>>> ast.parse("print('banana')") == ast.parse("print('banana' ) ")
False
>>> ast.compare(ast.parse("print('banana')"), ast.parse("print('banana' ) "))
True
# Unpacking 语法错误提示改进
# python 3.13
>>> a, b = 1, 2, 3
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<python-input-3>", line 1, in <module>
a, b = 1, 2, 3
^^^^
ValueError: too many values to unpack (expected 2)
# python 3.14
ValueError: too many values to unpack (expected 2, got 3)
# union 类型的统一
>>> int | str
int | str
# 3.13
>>> from typing import Union
>>> Union[int, str]
typing.Union[int, str]
# 3.14
>>> Union[int, str]
int | str